Acids are very familiar substances. They are characterized by having hydrogen atoms (red) bonded to very electronegative atoms such as oxygen (blue) o el cloro (green).
| CH3-COOH | (HOOC-CH2)2C(OH)COOH | HCl | CH3CH(OH)COOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid is in vinegar | Citric acid is in lemon or orange juices | Chlorhydric acid is in the gastric juice | Lactic acid is in milk |
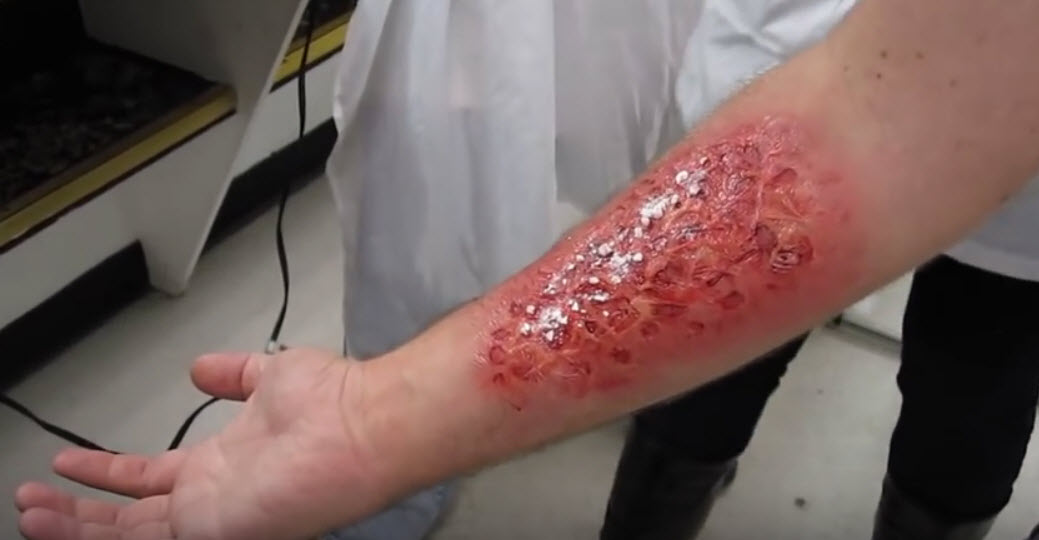 Simulated acid burning
Simulated acid burning
The two electrons of the bond are divided between the two initially bonded atoms. This cleavage is called homolytic and very difficult.
The two electrons in the bond stay on the side of the more electronegative atom of the two that formerly form the bond. This is the most common way of bond cleavage.
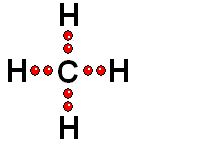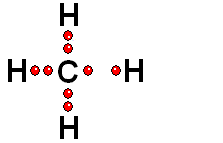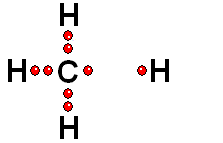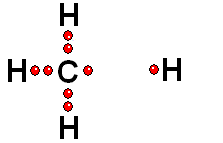
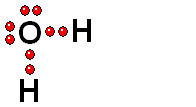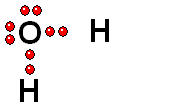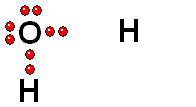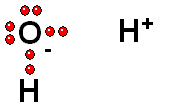
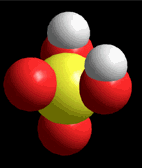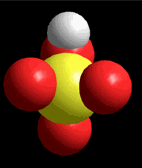 Model of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) losing a proton
Model of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) losing a proton
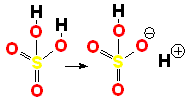 Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a very strong acid that loses a "proton" easily. When the molecule "keeps" the two electrons from the bond, it acquires a negative charge that offsets the positive charge of the "proton."
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a very strong acid that loses a "proton" easily. When the molecule "keeps" the two electrons from the bond, it acquires a negative charge that offsets the positive charge of the "proton."Bases are also very familiar substances. They are characterized by having very electronegative atoms such as oxygen (red) and nitrogen (blue) that can accept protons, even if they are already have some of them.
| NaOH | NH3 | NaCO3H | CaCO3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium hydroxide or "soda" is used used to unclog pipes | Ammonia is a cleaning product se usa como producto de limpieza | Sodium bicarbonate is a stomach antacid | Calcium carbonate is the main constituent of marble |
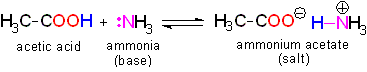 The acid loses a proton and the acid molecule (originally neutral) becomes negatively charged and becomes a base.
The acid loses a proton and the acid molecule (originally neutral) becomes negatively charged and becomes a base.