| K2O | NaI | Na2S | CaBr2 |
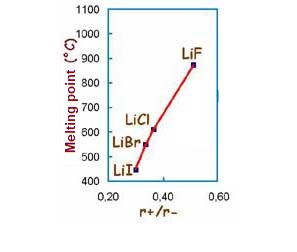
In an ionic structure, ions of opposite signs attract very strongly. That this force is very great is shown by the melting points of the ionic salts. For example, to melt common salt (NaCl) and convert it to a liquid state, about 800ºC is needed. This means a high amount of energy. The energy that must be supplied to an ionic compound to overcome the forces between the ions and be able to melt it is called lattice energy.