ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF ANHYDRIDES
Basicity of the Carbonyl Group
The basicity of a carbonyl group can be studied from the acidity of its protonated form.
The higher the acidity of the protonated form, the lower the starting carbonyl's basicity.
The higher the participation of the third resonance form, the more stable (less acidic) the protonated form of a carbonyl group. Hence, the higher the L group's ability to release electrons, the larger the carbonyl group's basicity.
Can you rationalize in the previous terms the following pKa values?
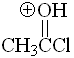 Acetyl chloride
Acetyl chloride
pKa = -9.0
Chlorine is highly electronegative thus making the protonated form the least stable in the series.
Acyl halides bear the least basic carbonyl group in the series.
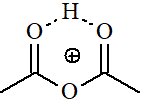 Acetic
Acetic
Anhydride
pKa = -8.5
The electronegativities of Cl and O-C=O should be very much alike. But in an anhydride there are two C=O groups and the protonation probability doubles. On the other hand, the protonated species should be additionally stabilized by the hydrogen bonding shown. All that should account for the slightly higher basicity of anhydrides as compared to acyl chlorides.
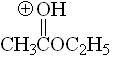 Ester
Ester
pKa = -6.5
The alkoxy group can stabilize the positive charge by mesomeric effect and the third resonance form makes full sense.
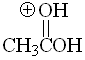 Acid
Acid
pKa = -6.0
The fact that, in a protonated carboxylic acid, the first and third resonance forms are equivalent gives an extra of stabilization. That avails for the paradox that a carboxylic acid is the most basic species of this series.
The alpha hydrogens to a carbonyl group are always feebly but usefully acidic, due to the delocalization of the negative charge. Has anything to do the L group with this?
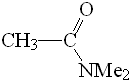 DMF
DMF
pKa = 30
Amides have the least acidic alpha hydrogens due to the strong electron-releasing effect of the NMe2 group that destabilizes the anionic form.
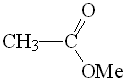 Methyl acetate
Methyl acetate
pKa = 25
The higher electronegativity of the OMe group allows us to explain the higher acidity of the ester's alpha hydrogen as compared to amide's.
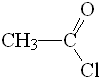 Acetyl chloride
Acetyl chloride
pKa = 16
Among the these compounds, the acid chloride displays the lowest pKa values and thus bears the most acidic alpha hydrogens as a consequence of the highest electronegativity of Cl. The more electronegative the L group, the higher the stabilization of the anion and the more acidic the alpha hydrogens.
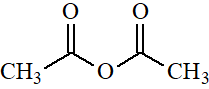 Acetic Anhydride
Acetic Anhydride
pKa = 16
Anhydrides and acyl chlorides are very much alike because the electronegativities of Cl and O-C=O groups are very similar.
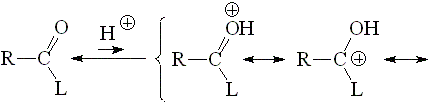
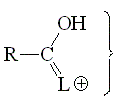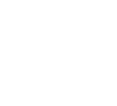
 Acetic
Acetic Acetic Anhydride
Acetic Anhydride