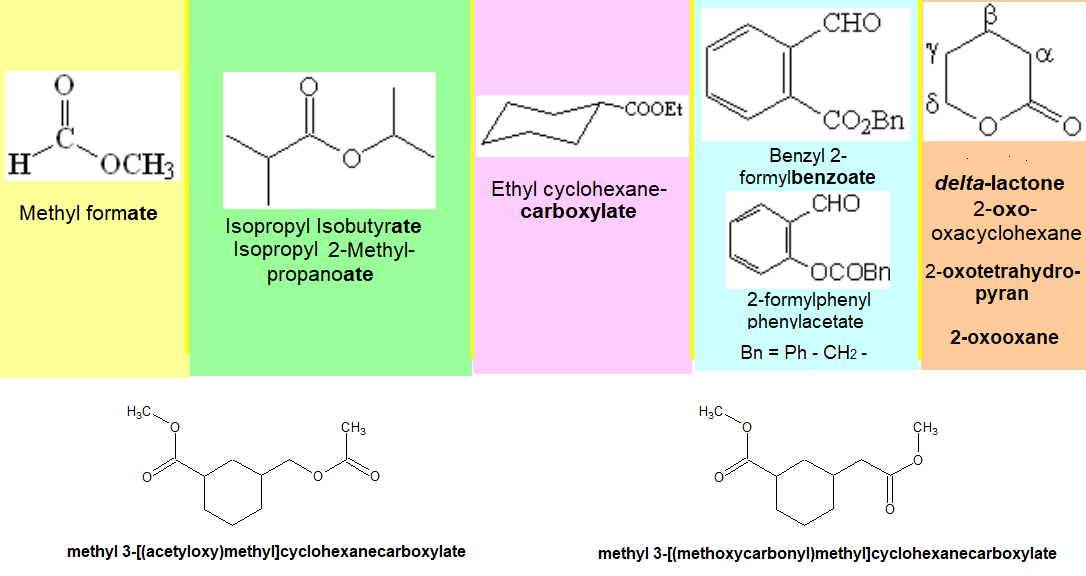
Nomenclature rules are complex. We will only attemp to give names to relatively simple molecules. Look at the following examples of representative molecules bearing ester groups.
An ester comes from the condensation of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol (acid + alcohol = ester + water). Analogously to the inorganic salts (acid + base = salt + water), esters are named as if they were acid salts (carboxylates), the imaginary counterion being an alkyl radical.
The ester function is almost always the principal one.
When it isn't, it is named as alkyloxycarbonyl or alkylcarbonyloxy, depending on whether it is bonded to the main chain by the carbonyl group or by the alcohol oxygen, respectively.
As usual, in both moieties (that derived from the acid and the other from the alcohol) the longest possible chain containing the largest possible number of other functions is selected.
The main chain is ended by the sufix "ate" or "carboxylate".
The numbering starts by the ester function.