EMISSION OF THE PERTURBED NUCLEI
In the previous section we left the methane molecules within an intense, external magnetic field (Ho) and we irradiated the system, for enough time, with an electromagnetic wave B1.
The outcome of this perturbation was that the macroscopic magnetization of equilibrium (M0) was transferred to the x,y plane. It now starts our "listening" to the NMR signal.
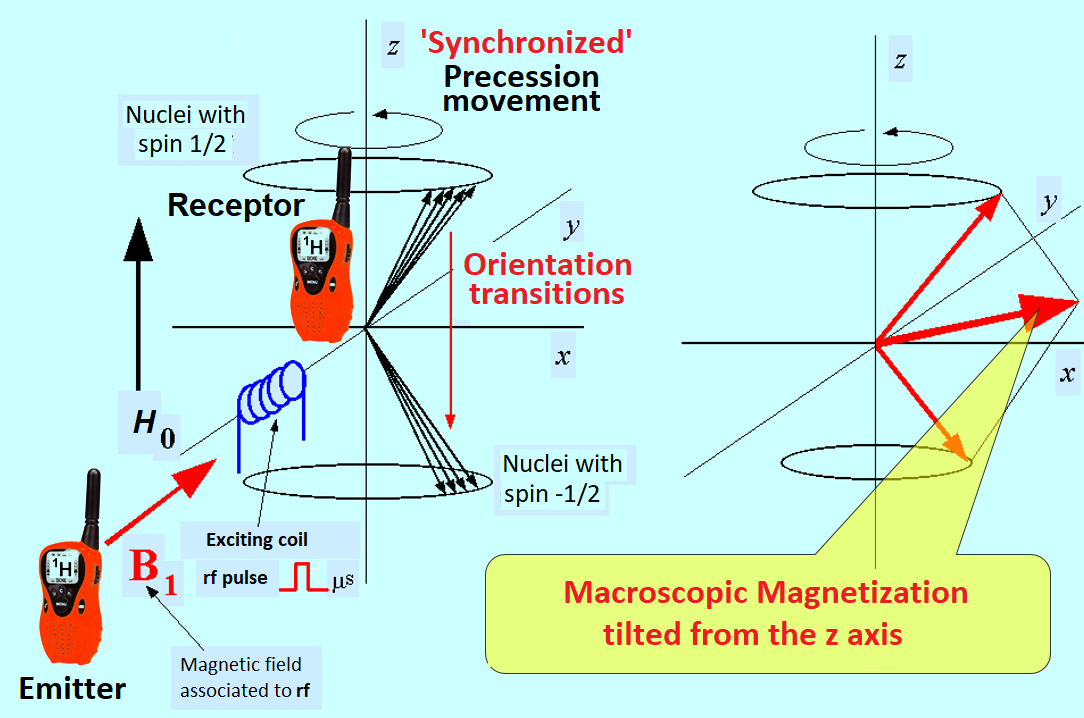 Scheme of the necessary perturbation in order to start "listening" to the NMR signal.
Scheme of the necessary perturbation in order to start "listening" to the NMR signal.
 Evolución del vector de magnetización transversal (Mxy) una vez detenida la perturbación.
Evolución del vector de magnetización transversal (Mxy) una vez detenida la perturbación.
As we stated before, an unaligned magnetic vector, relative to an external magnetic field, starts spinning around the latter.
Therefore, the "transversal magnetization" (Mxy) starts spinning in the x,y plane and emmits a signal that is received by our “walkie-talkie” receptor connected to the computer.
How does the signal look like?
Since the received signal depends on the particular perturbed nucleus, the precession frequency of Mxy will be, in a 1.81 Tesla field, of 80 MHz had 1H been excited or 20 MHz if it was 13C.
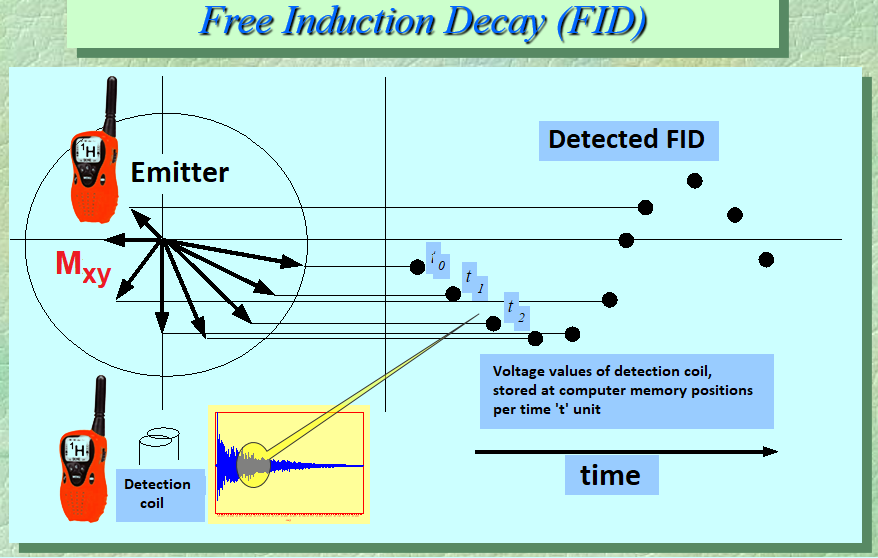
The main feature of the received signal is that it decays with time because the system tends to recover the equlibrium starting situation where, simply speaking, Mxy didn't exist.
That's why the received signal is called FID, acronym of “Free Induction Decay”.
A FID is a periodic signal, with a frequency of 80 MHz for 1H or 20 MHz for 13C (in a 1.81 Tesla field) that extinguises in several seconds.
If we repeat the process, get several FID's and add them together, the sensitivity of the NMR signal will be spectacularly enhanced.
Last but not least, please notice that the FID is a time-domain signal, because it is the mere evolution of a voltage with time, that our "walkie-talkie” receptor transferred to the computer that finally digitalized it.
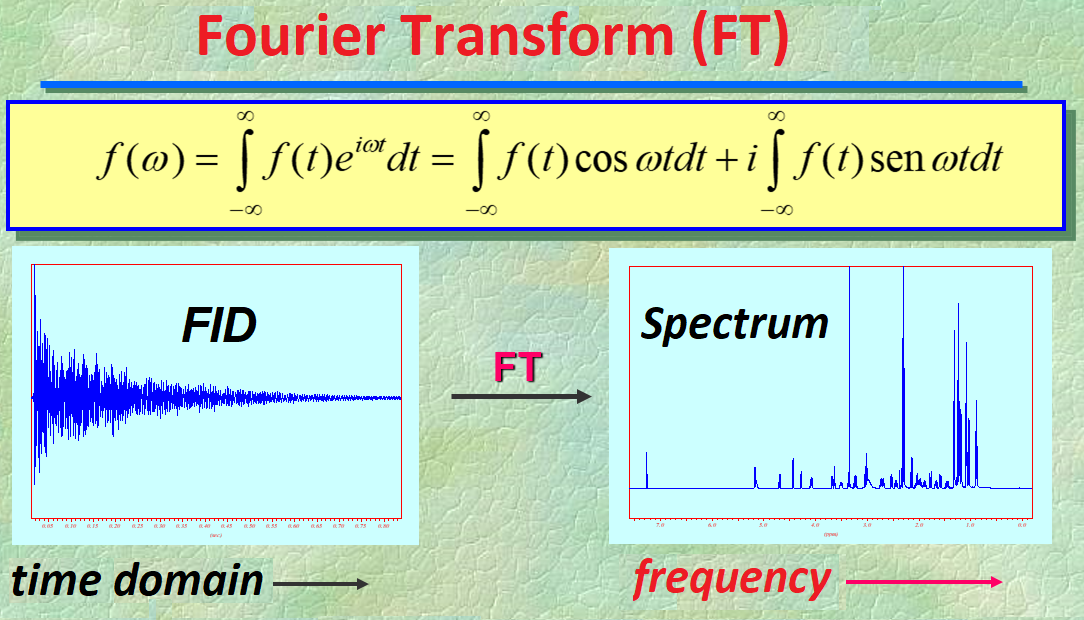 Fourier Transformation of the FID in order to translate the initial time-domain NMR signal into a more meaningful frequency-domain spectrum.
Fourier Transformation of the FID in order to translate the initial time-domain NMR signal into a more meaningful frequency-domain spectrum.
Fourier Transform is a mathematical function that translates the initial time-domain NMR signal (FID) into a more meaningful frequency-domain spectrum.
This is the certainly complex way of obtaining a NMR spectrum which is a plot of signals on a frequency scale.
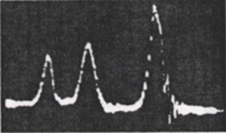
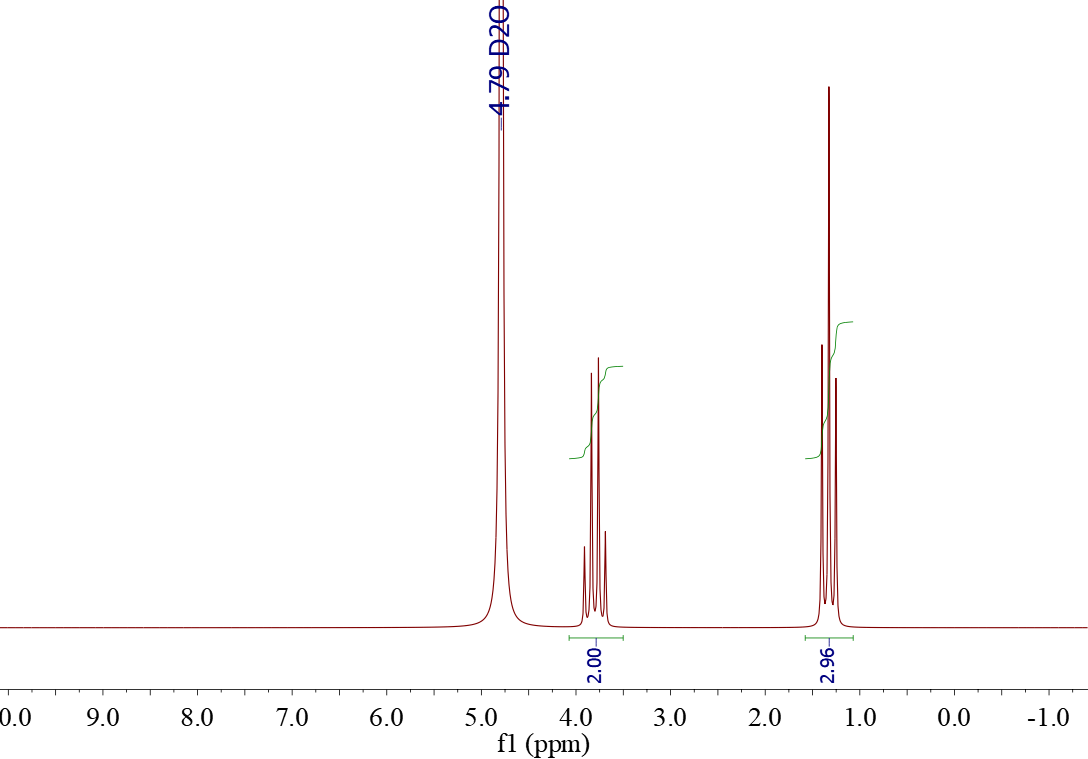
Do you remeber the primitive spectrum of ethanol? Compare it with one of its modern versions.
We'll start practicing with spectra right away!!!
 Scheme of the necessary perturbation in order to start "listening" to the NMR signal.
Scheme of the necessary perturbation in order to start "listening" to the NMR signal.
 Evolución del vector de magnetización transversal (Mxy) una vez detenida la perturbación.
Evolución del vector de magnetización transversal (Mxy) una vez detenida la perturbación.
 Fourier Transformation of the FID in order to translate the initial time-domain NMR signal into a more meaningful frequency-domain spectrum.
Fourier Transformation of the FID in order to translate the initial time-domain NMR signal into a more meaningful frequency-domain spectrum.