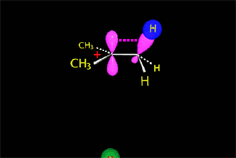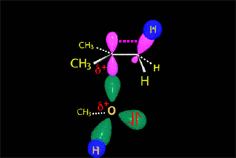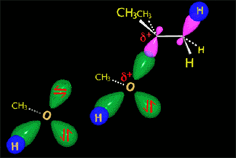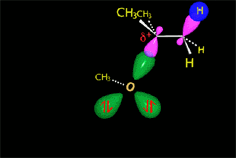
From the reactants (red plateau), the three processes - bimolecular substitution (blue pathway), bimolecular elimination (green pathway) and carbocation fomation (gray pathway) - simultaneously happen.
The carbocation (yellow plateau) can evolved by two different routes, unimolecular substitution (brown pathway) and unimolecular elimination (navy-blue pathway).
The fastest pathway and therefore the predominat one will be that taking place through the lowest energy TS.
The relative energy height of the different TS's depends on:
- Reactants structure
- Nucleophilicity/Basicity of the nucleophile/base
- Polarity of the solvent
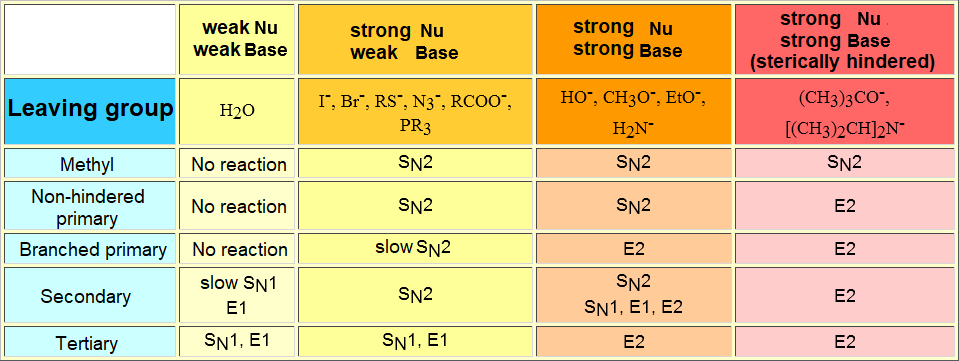
It is always difficult to predict what would happen in a reaction, the following table gives some rules of thumb depending on the general structure of the reactant bearing the leaving group and the nucleophile/base.
In the case of the nucleophiles HO-, CH3O-, EtO-, H2N-,(CH3)3CO-, the solvent is usually the corresponding conjugate acid.
In the remaining cases the solvent used is a non-protic, polar one like dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide or acetone.
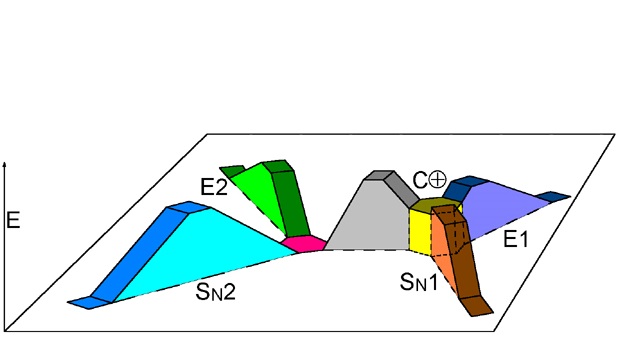
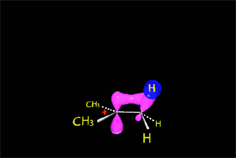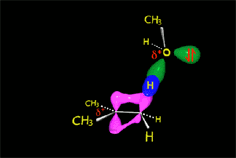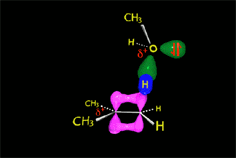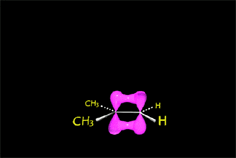 E1
E1
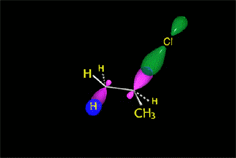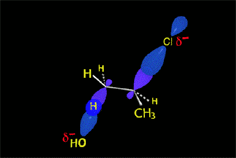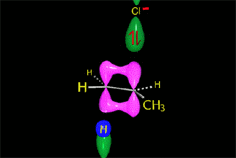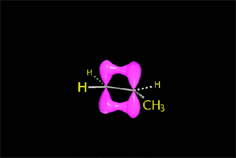 E2
E2
 C+
C+

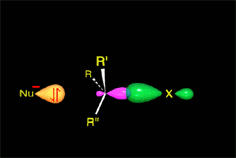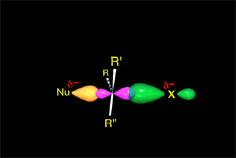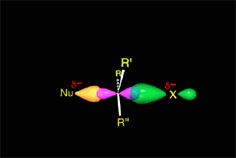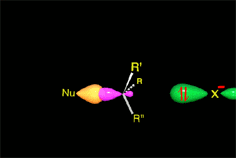 SN2
SN2