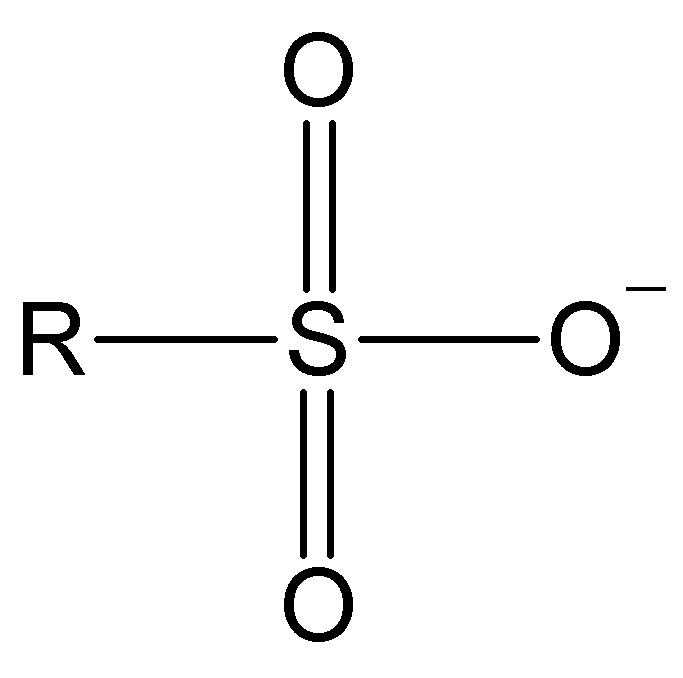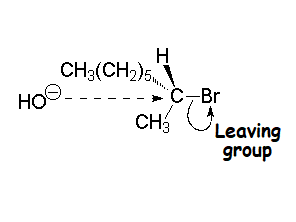
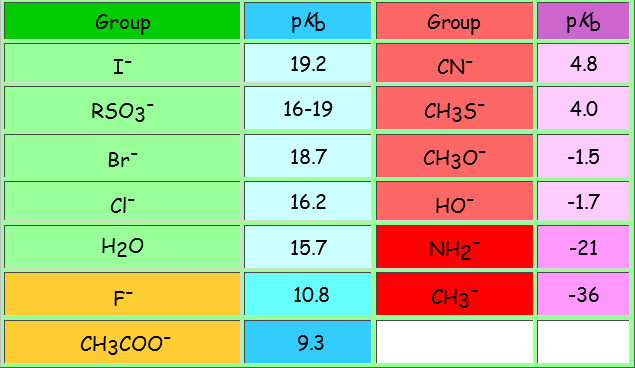
| SIZE | ELECTRONEGATIVITY | DELOCALIZATION |
|---|---|---|
| The larger the atom, the more disperse and stable the excess electron density and the lower its basicity. This is the predominant factor in alkyl halides: larger size I- > Br- > Cl- > F-smaller size tamaño weaker base I- < Br- < Cl- < F- stronger base better leaving group I- > Br- > Cl- > F- worse leaving group | Comparing atoms belonging to the same row in the Periodical System, the higher the electronegativity of the atom bearing the excess electron density, the lower its basicity and the better its capabilities as leaving group. In the halides, the size effect is predominant because from one halide to the next we must change rows. From a really bad leaving group F- > HO- > NH2- > CH3- to the worst leaving group ever | Resonance allows for the heavy delocalization of excess electron density and its strong stabilization. That's why the sulfonates are extremely weak bases and thus excellent leaving groups. |