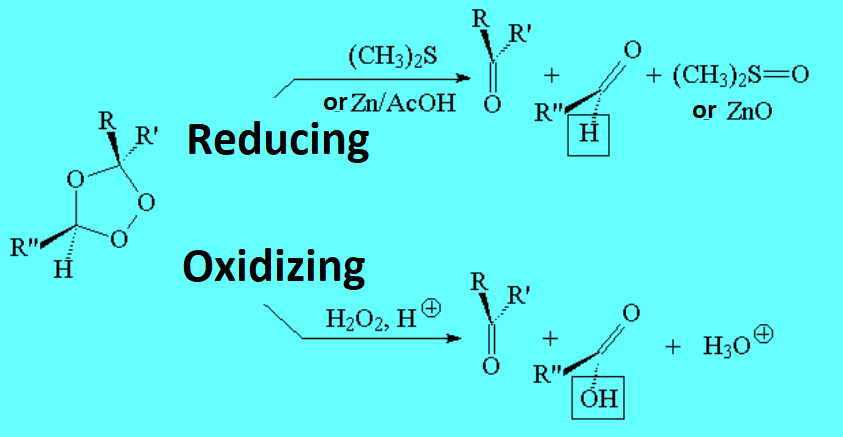
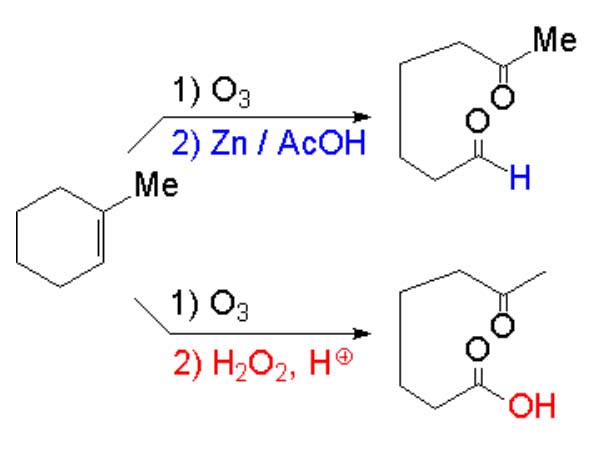
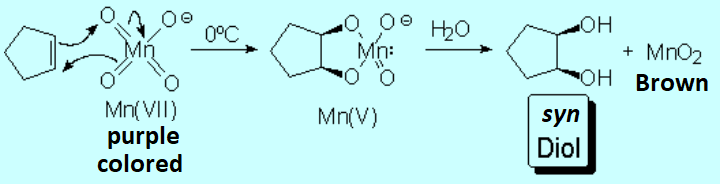
The carbons of olefins are in a relatively low oxidation state and they can thus be transformed in other more oxidized substances. Olefin oxidation can be carried out gently or vigorously, with different outcome.
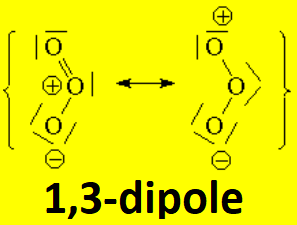
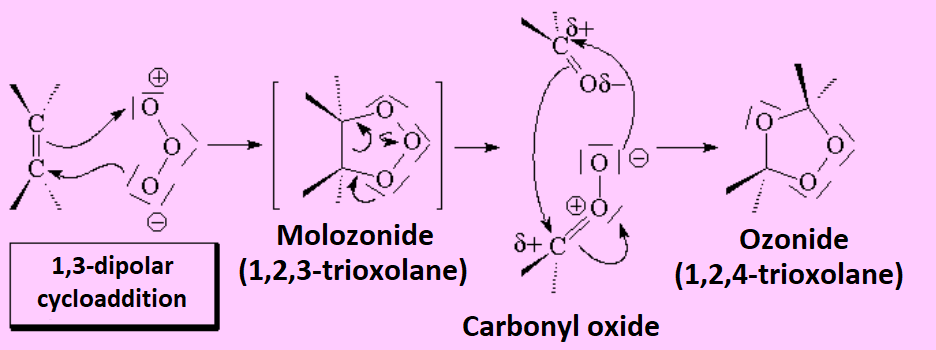
The reaction of ozone with a given olefin goes through a complicated mechanism that implies a very important type of reaction in organic chemistry, the so-called 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, as a consequence of ozone's electronic structure:

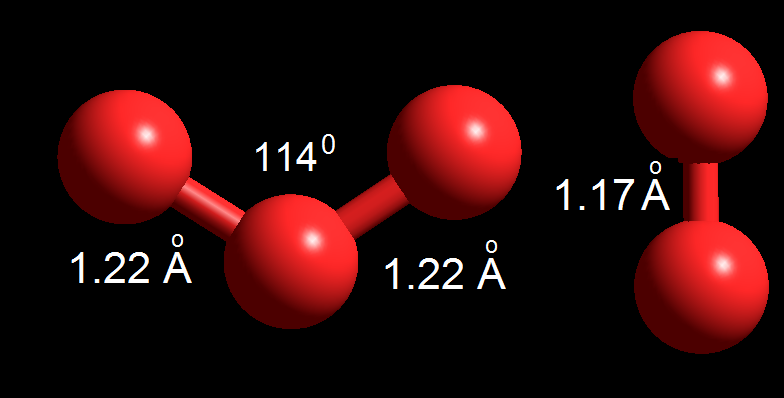 Comparison between the size and shape of ozone and oxygen.
Comparison between the size and shape of ozone and oxygen.