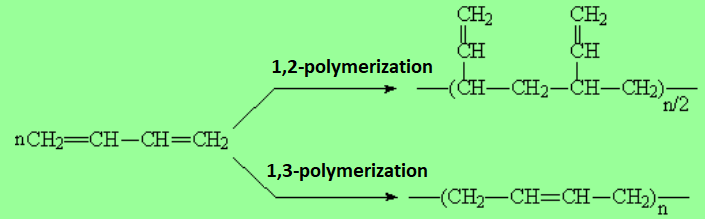
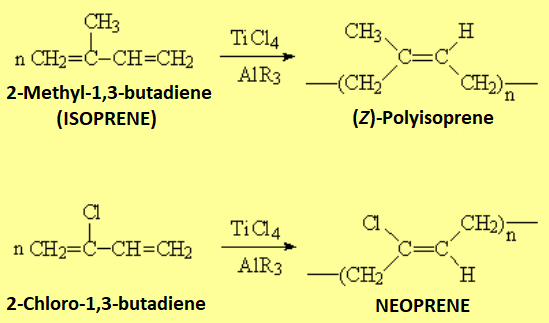
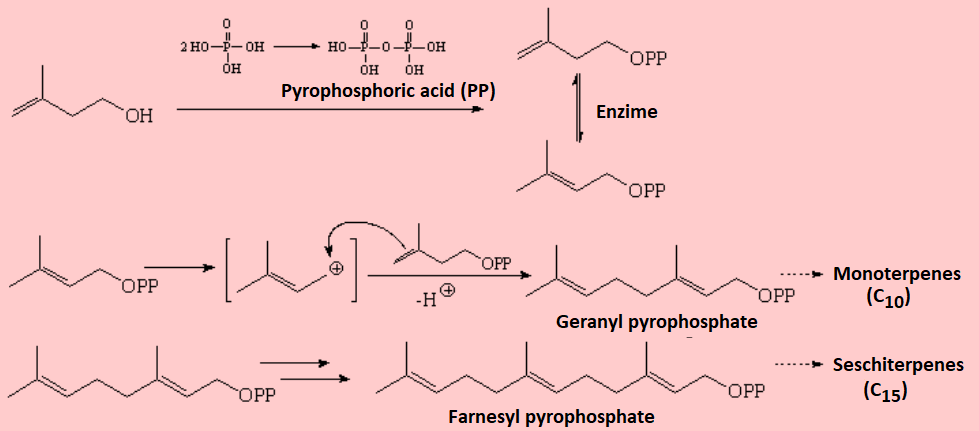
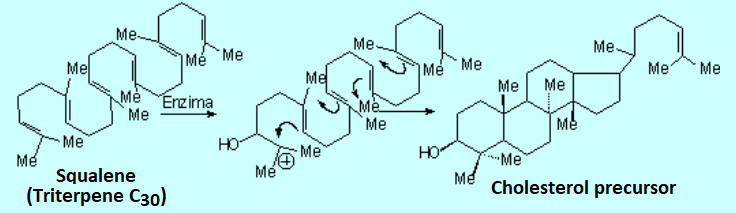
Similarly to alkenes, polyenes may undergo polymerization.
For example, 1,3-butadiene can polymerize either by normal (1,2) or conjugated (1,3) addition.
The two processes lead to different polymers, more or less branched, with different physical and chemical properties.
Polymerization controlled by Ziegler-Natta catalysis yields polymers of everyday use (tyres, coatings, etc).
In order to give additional elasticity to these polymers, vulcanization is performed. This procedure consists of the treatment of the polymer with sulfur under heating. The polymer chains end up interconnected by polysulfur bridges that gives added elasticity to it.
It is believed that some natural products essential to life, like cholesterol or in general the family of terpenes, are produced by biologically controlled polymerization of polyenic systems: