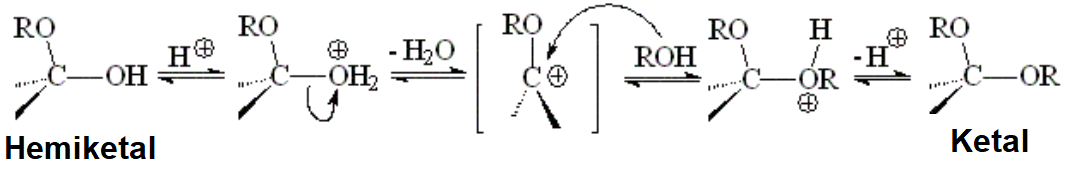
In a ketal, the former carbon of the C=O loses the pi cloud and turns its hybridization into sp3.
Hence, the ketal is way less reactive than the initial aldehyde or ketone.
A ketal endures the attack of numerous nucleophiles that would easily react with a double C=O bond.