ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF ESTERS
Carbonyl Group's Basicity
The basicity of a carbonyl group can be studied from the acidity of its protonated form.
The higher the acidity of the protonated form, the lower the starting carbonyl's basicity.
The higher the participation of the third resonance form, the more stable (less acidic) the protonated form of a carbonyl group. Hence, the higher the L group's ability to release electrons, the larger the carbonyl group's basicity.
Can you rationalize in the previous terms the following pKa values?
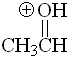 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
pKa = -8.0
The third resonance form is not possible when L = H. The protonated form is thus very unstable. Aldehydes are the least basic in the series.
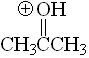 Ketone
Ketone
pKa = -7.2
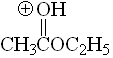 Ester
Ester
pKa = -6.5
The alkoxy group can stabilize the positive charge by mesomeric effect and the third resonance form makes full sense. That's why esters are more basic than ketones.
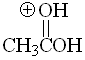 Acid
Acid
pKa = -6.0
The fact that, in a protonated carboxylic acid, the first and third resonance forms are equivalent gives an extra of stabilization. That avails for the paradox that a carboxylic acid is the most basic species of this series.
As in aldehydes and ketones, the alpha hydrogens to an ester are feebly but usefully acidic, due to the delocalization of the negative charge towards the carbonyl group.
Has anything to do the L group with this?
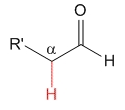 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
pKa = 17
Aldehyde's hydrogen does not exert any special effect and pKa = 17 can be taken as a reference acidity value for the alpha hydrogens to a carbonyl group.
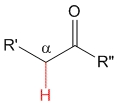 Ketone
Ketone
pKa = 20
Alkyl groups are electron releasing by inductive effect and therefore they destabilize the anion, thus making ketones' alpha hydrogens less acidic than aldehydes'.
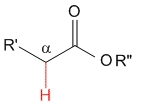 Ester
Ester
pKa = 25
Alkoxy groups are strong electron releasing by mesomeric effect and destabilize the anion even further, thereby causing the lowest acidity for esters in the studied series.
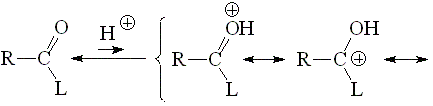
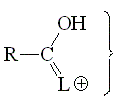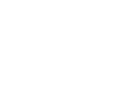
 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
 Ketone
Ketone
 Ester
Ester