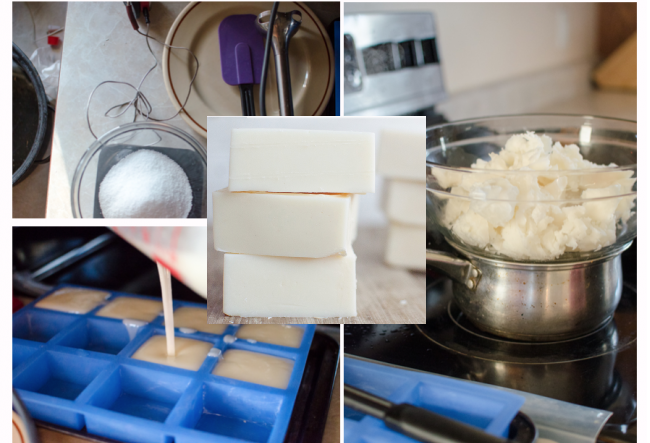
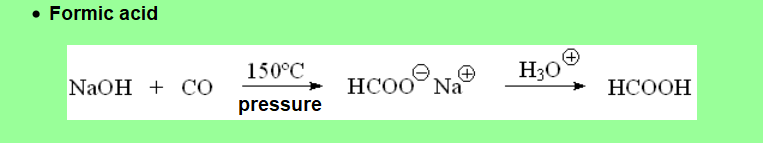
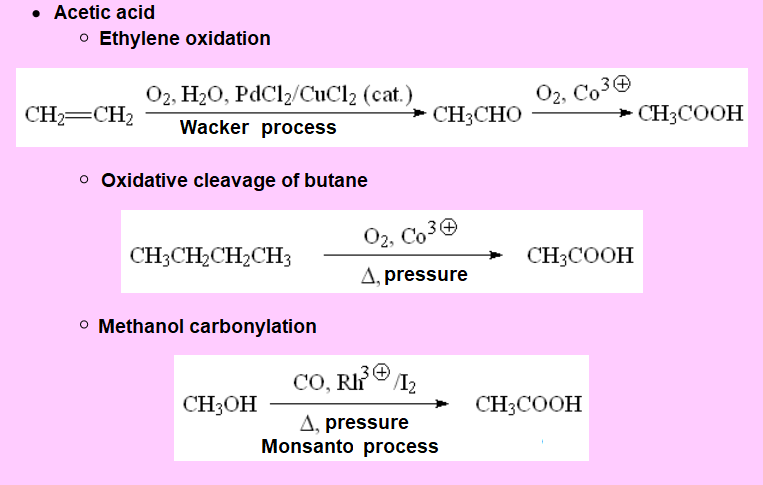
Many carboxylic acids can be obtained from natural sources like, for example, vegetal edible oils.
The preparation of soap from them, an experiment that you could easily carry out at home, involves the preparation and isolation of the sodium salt of long chain carboxylates.
Lipids, triglycerides or fats are triple esters of glycerine that are found either in vegetal (olive, sunflower, etc.) or animal (tallow, lard, butter, etc.) edible oils and fats.
These esters break down (hydrolysis) in basic medium. This process is called saponification ("sapo" formation from latin and greek roots).
In general, when one saponifies an ester, an alcohol and a carboxylate are produced.
In this case the alcohol is 1,2,3-propanetriol (glycerin).
In general, when one saponifies an ester, an alcohol and a carboxylate are produced.
In this case the carboxylate is cis-9-octadecenoate (oleate).
Its neutralization with mineral acid yields oleic acid, one of the most important and ubiquituous fatty acids.