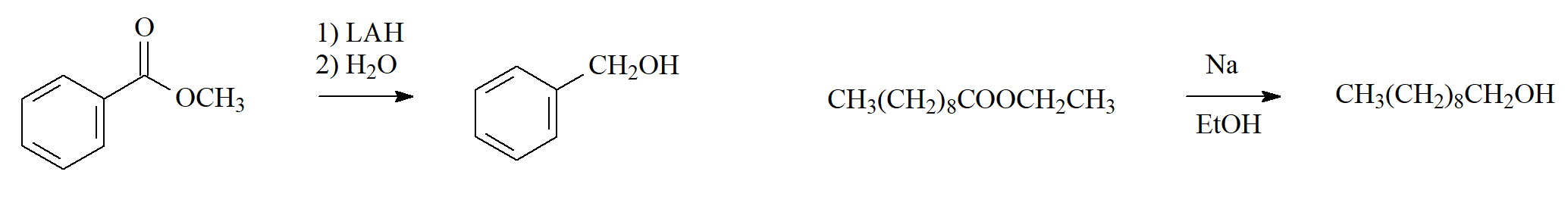Esters are fairly reactive due to the electrophilicity of the C=O carbon and to its capacity to stabilize alpha enolate anions.
This reaction is the reverse of Fischer's esterification and its mechanism is the same but inverting the sequence (Principle of Microscopic Reversibility).
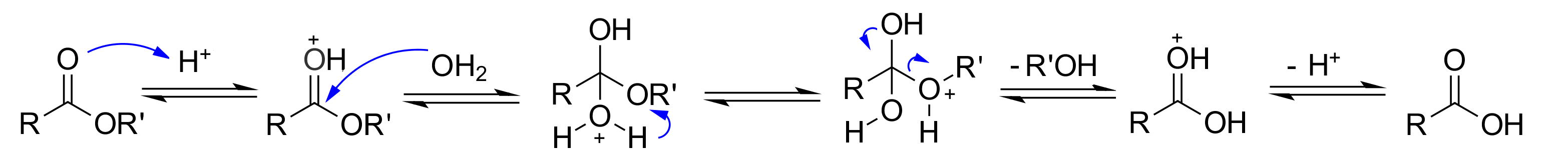
The mechanism is the typical addition-elimination activated by the early protonation of the C=O group.
If one uses isotopically labelled water with "18O" the alcohol ends up free of radiation clearly indicating that the O-CH3 bond never breaks and reinforcing the addition-elimination mechanism.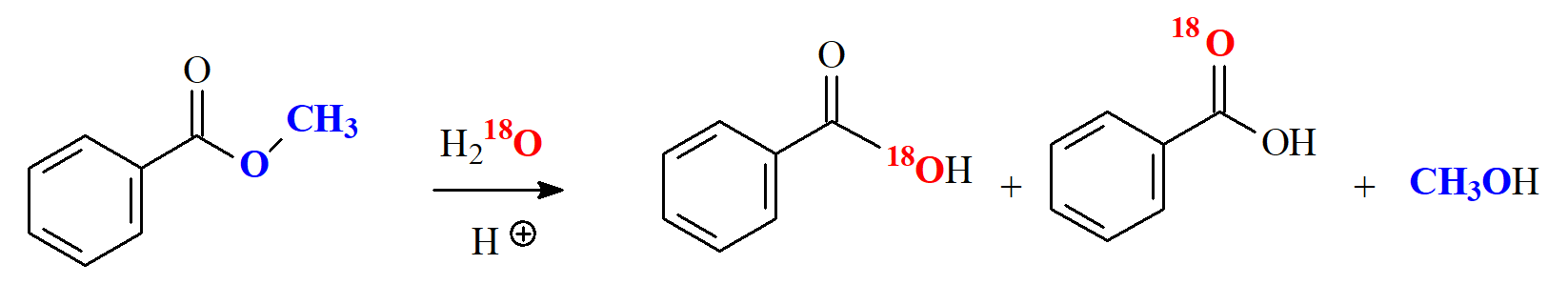
Basic Hydrolysis (Saponification)
"Saponification" means "making soap". The saponification of fats and oils is the method of choice to obtain long-chain carboxylates.
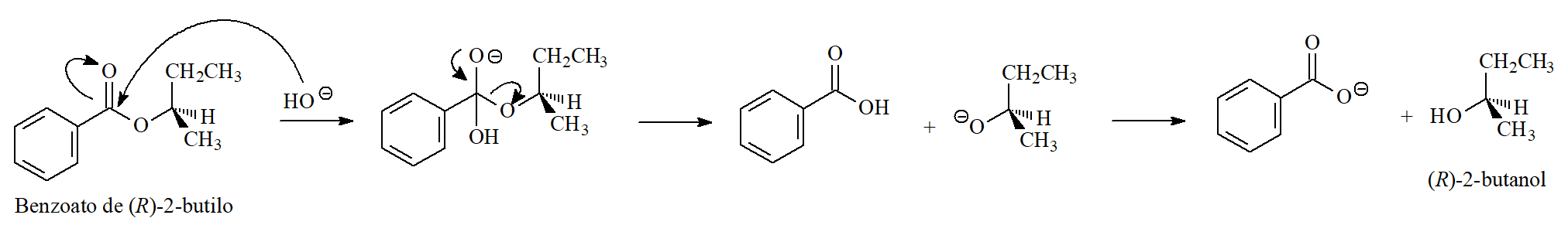
In the following example the chirality of the alcoholic moiety remains intact strongly pointing to the addition-elimination mechanism and that the O-CH bond never breaks.
If hydroxide had attacked the butyloxy group, the leaving alcohol would have either inverted via a SN2 process or racemized via a SN1 mechanism.
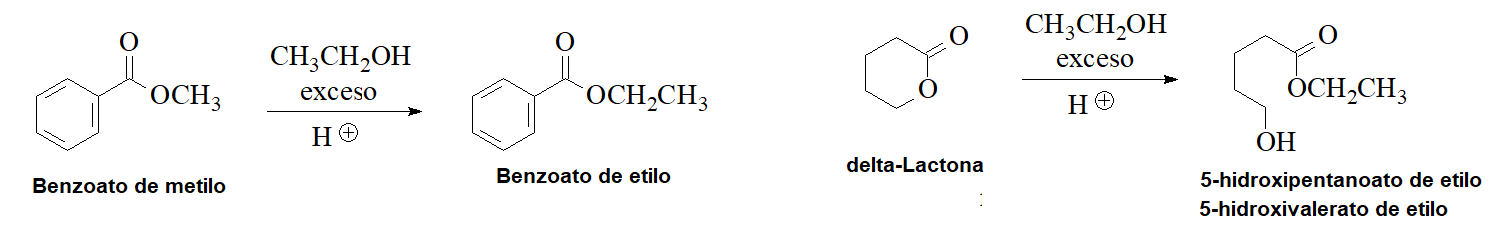
Transesterification
An ester can be turned into another one by its dissolving in an alcohol in acidic medium. Look to some examples:
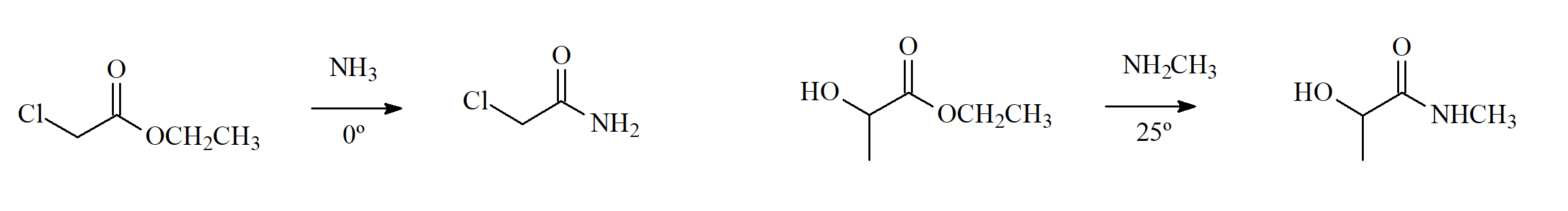
Ammonia and amines (with N), either primary or secondary, are excellent nucleophiles that may react with esters yielding amides (with D).
Would you propose an addition-elimination mechanism for this process?
Hydride Reduction or Metal Reduction
Esters are reduced only with strong hydrides like LiAlH4 (LAH).
NaBH4 DOES NOT REACT.
Alkaline metals can also be used.
IMPORTANT: Beware of other group's competition!
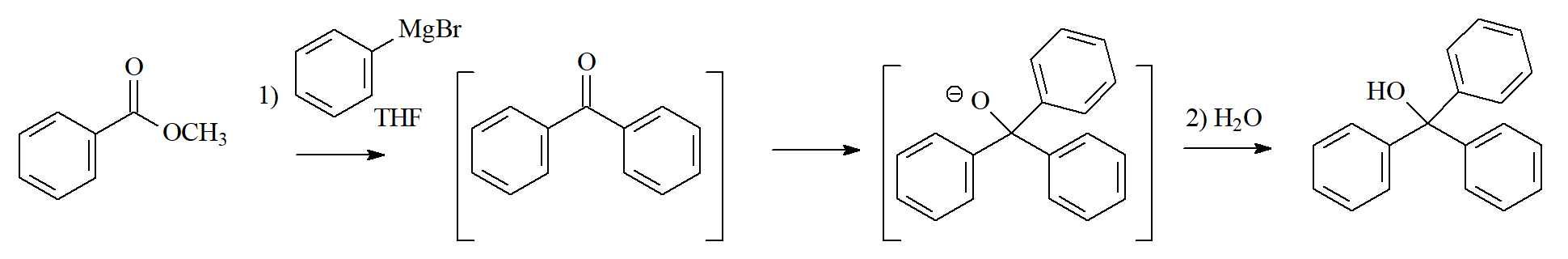
Organolithium or Grignard Reagents
Organometallics react with esters through the addition-elimination mechanism but there's a glitch: the intermediate ketone reacts even faster than the starting ester and the reaction cannot be stopped and leads to the secondary alcohol. Look at an example below.
IMPORTANT: Beware of other group's competition!
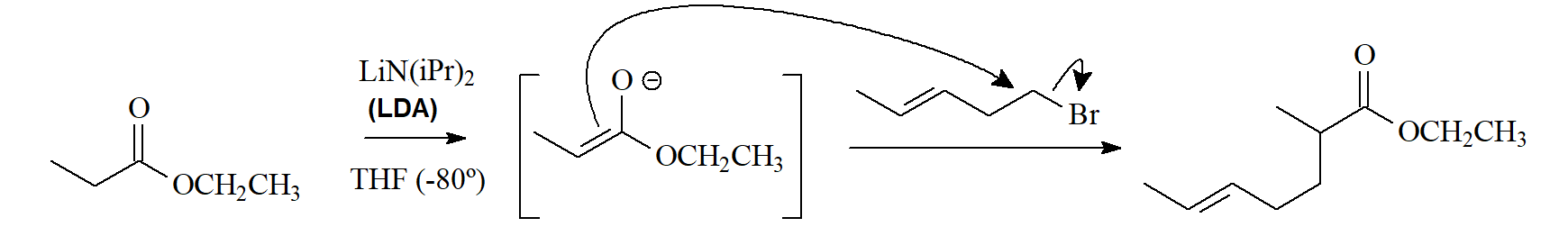
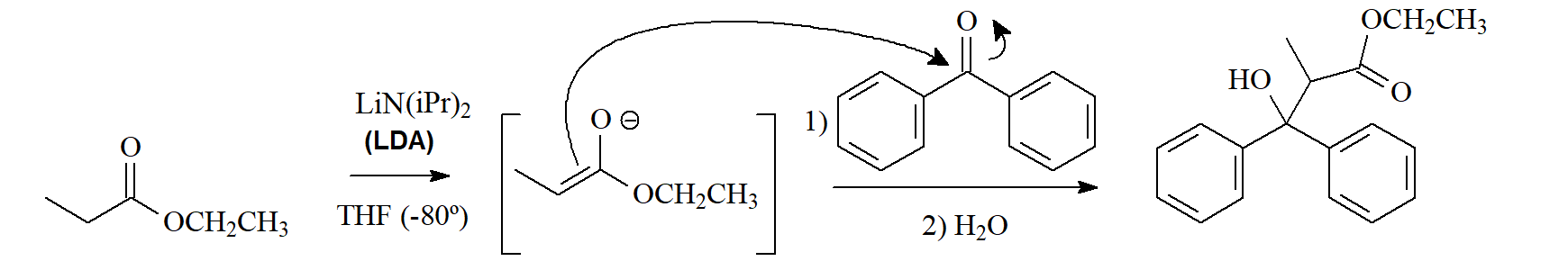
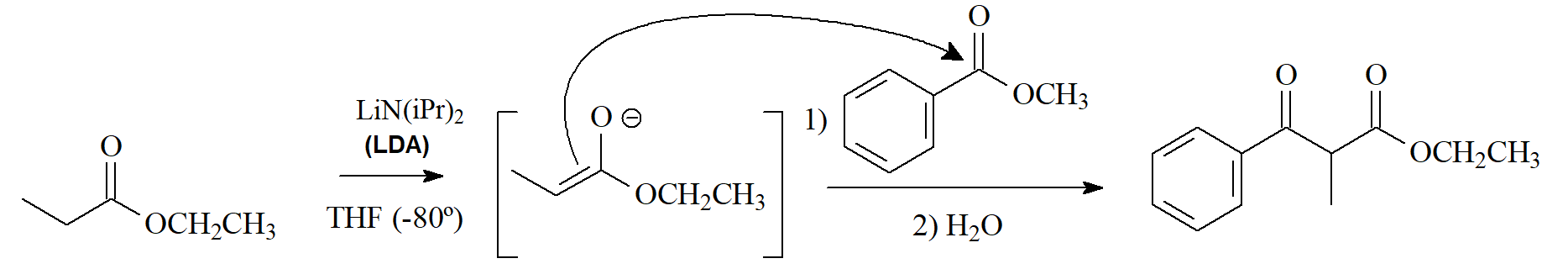
The enolate ions of esters can undergo various reactions:
1) SN (alkylation) with compounds bearing a good leaving group.
2) addition to other carbonyl groups.
3) addition-elimination to esters (Claisen condensation)
Claisen condensation is to esters what aldol condensation is to aldehydes and ketones.
It is very important a reaction because it leads to beta-dicarbonyl compounds, very versatile in organic synthesis.
Dieckmann condensation is the INTRAmolecular version of Claisen condensation.
It is very important a reaction because it leads to cyclic beta-dicarbonyl compounds, very versatile in organic synthesis.